The Indus Valley civilization, one of the world's oldest, flourished during the 3rd and 2nd millennia B.C. and extended into northwestern India. Aryan tribes from the northwest infiltrated the Indian subcontinent about 1500 B.C.; their merger with the earlier Dravidian inhabitants created the classical Indian culture. The Maurya Empire of the 4th and 3rd centuries B.C. - which reached its zenith under ASHOKA - united much of South Asia. The Golden Age ushered in by the Gupta dynasty (4th to 6th centuries A.D.) saw a flowering of Indian science, art, and culture. Islam spread across the subcontinent over a period of 700 years. In the 10th and 11th centuries, Turks and Afghans invaded India and established the Delhi Sultanate. In the early 16th century, the Emperor BABUR established the Mughal Dynasty, which ruled India for more than three centuries. European explorers began establishing footholds in India during the 16th century.
By the 19th century, Great Britain had become the dominant political power on the subcontinent and India was seen as the "Jewel in the Crown" of the British Empire. The British Indian Army played a vital role in both World Wars. Years of nonviolent resistance to British rule, led by Mohandas GANDHI and Jawaharlal NEHRU, eventually resulted in Indian independence in 1947. Large-scale communal violence took place before and after the subcontinent partition into two separate states - India and Pakistan. The neighboring nations have fought three wars since independence, the last of which was in 1971 and resulted in East Pakistan becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh. India's nuclear weapons tests in 1998 emboldened Pakistan to conduct its own tests that same year. In November 2008, terrorists originating from Pakistan conducted a series of coordinated attacks in Mumbai, India's financial capital. Despite pressing problems such as significant overpopulation, environmental degradation, extensive poverty, and widespread corruption, economic growth following the launch of economic reforms in 1991 and a massive youthful population are driving India's emergence as a regional and global power.
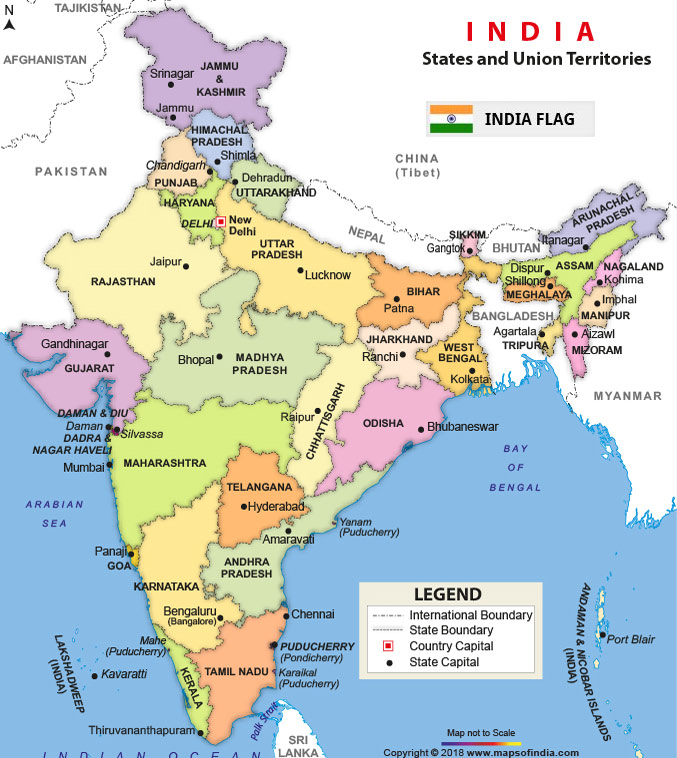
| Geography : INDIA |
| |
| Location : |
| |
| Southern Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and Pakistan |
| |
| Geographic coordinates: |
| |
| 20 00 N, 77 00 E |
| |
| Map references: |
| |
| Asia |
| |
| Area: |
| |
total: 3,287,263 sq km
land: 2,973,193 sq km
water: 314,070 sq km |
| |
| Land boundaries: |
| |
total: 13,888 km
border countries (6): Bangladesh 4142 km, Bhutan 659 km, Burma 1468 km, China 2659 km, Nepal 1770 km, Pakistan 3190 km |
| |
| Coastline: |
| |
| 7,000 km |
| |
| Maritime claims: |
| |
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin |
| |
| Climate: |
| |
| varies from tropical monsoon in south to temperate in north |
| |
| Terrain: |
| |
| upland plain (Deccan Plateau) in south, flat to rolling plain along the Ganges, deserts in west, Himalayas in north |
| |
| Elevation: |
| |
mean elevation: 160 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: Kanchenjunga 8,586 m |
| |
| Natural resources: |
| |
| coal (fourth-largest reserves in the world), antimony, iron ore, manganese, mica, bauxite, rare earth elements, titanium ore, chromite, natural gas, diamonds, petroleum, limestone, arable land |
| |
| Land use: |
| |
agricultural land: 60.5% (2011 est.)
arable land: 52.8% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 4.2% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 3.5% (2011 est.)
forest: 23.1% (2011 est.)
other: 16.4% (2011 est.) |
| |
| Irrigated land: |
| |
| 667,000 sq km (2012) |
| |
| Population distribution: |
| |
| with the notable exception of the deserts in the northwest, including the Thar Desert, and the mountain fringe in the north, a very high population density exists throughout most of the country; the core of the population is in the north along the banks of the Ganges, with other river valleys and southern coastal areas also having large population concentrations |
| |
| Natural hazards: |
| |
droughts; flash floods, as well as widespread and destructive flooding from monsoonal rains; severe thunderstorms; earthquakes
volcanism: Barren Island (354 m) in the Andaman Sea has been active in recent years |
| |
| Environment - current issues: |
| |
| deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; desertification; air pollution from industrial effluents and vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage and runoff of agricultural pesticides; tap water is not potable throughout the country; huge and growing population is overstraining natural resources; preservation and quality of forests; biodiversity loss |
| |
| Environment - international agreements: |
| |
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| |
| Geography - note: |
| |
| dominates South Asian subcontinent; near important Indian Ocean trade routes; Kanchenjunga, third tallest mountain in the world, lies on the border with Nepal |
| |
| |
| People and Society : INDIA |
| |
| Population: |
| |
| 1,296,834,042 (July 2018 est.) |
| |
| Nationality: |
| |
noun: Indian(s)
adjective: Indian |
| |
| Ethnic groups: |
| |
| Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3% (2000) |
| |
| Languages: |
| |
Hindi 43.6%, Bengali 8%, Marathi 6.9%, Telugu 6.7%, Tamil 5.7%, Gujarati 4.6%, Urdu 4.2%, Kannada 3.6%, Odia 3.1%, Malayalam 2.9%, Punjabi 2.7%, Assamese 1.3%, Maithili 1.1%, other 5.6% (2011 est.)
note: English enjoys the status of subsidiary official language but is the most important language for national, political, and commercial communication; there are 22 other officially recognized languages: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu; Hindustani is a popular variant of Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern India but is not an official language |
| |
| Religions: |
| |
| Hindu 79.8%, Muslim 14.2%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.7%, other and unspecified 2% (2011 est.) |
| |
| Age structure: |
| |
- 0-14 years: 26.98% (male 185,736,879 /female 164,194,080)
- 15-24 years: 17.79% (male 122,573,662 /female 108,109,968)
- 25-54 years: 41.24% (male 276,283,581 /female 258,563,835)
- 55-64 years: 7.6% (male 49,334,703 /female 49,197,817)
- 65 years and over: 6.39% (male 39,184,523 /female 43,654,994) (2018 est.)
|
| |
| Dependency ratios: |
| |
- total dependency ratio: 52.2 (2015 est.)
- youth dependency ratio: 43.6 (2015 est.)
- elderly dependency ratio: 8.6 (2015 est.)
- potential support ratio: 11.7 (2015 est.)
|
| |
| Median age: |
| |
- total: 28.1 years
- male: 27.5 years
- female: 28.9 years (2018 est.)
|
| |
| Population growth rate: |
| |
| 1.14% (2018 est.) |
| |
| Birth rate: |
| |
| 18.7 births/1,000 population (2018 est.) |
| |
| Death rate: |
| |
| 7.3 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.) |
| |
| Net migration rate: |
| |
| 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.) |
| |
| Population distribution: |
| |
| with the notable exception of the deserts in the northwest, including the Thar Desert, and the mountain fringe in the north, a very high population density exists throughout most of the country; the core of the population is in the north along the banks of the Ganges, with other river valleys and southern coastal areas also having large population concentrations |
| |
| Urbanization: |
| |
urban population: 34% of total population (2018)
rate of urbanization: 2.37% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.) |
| |
| Major urban areas - population: |
| |
| 28.514 million NEW DELHI (capital), 19.98 million Mumbai, 14.681 million Kolkata, 11.44 million Bangalore, 10.456 million Chennai, 9.482 million Hyderabad (2018) |
| |
| Sex ratio: |
| |
- at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- 0-14 years: 1.13 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- 15-24 years: 1.13 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- 25-54 years: 1.06 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- 55-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- 65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
- total population: 1.08 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
|
| |
| Maternal mortality rate: |
| |
| 174 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.) |
| |
| Infant mortality rate: |
| |
- total: 37.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)
- male: 36.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)
- female: 39.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)
|
| |
| Life expectancy at birth: |
| |
- total population: 69.1 years (2018 est.)
- male: 67.8 years (2018 est.)
- female: 70.5 years (2018 est.)
|
| |
| Total fertility rate: |
| |
| 2.4 children born/woman (2018 est. |
| |
| |
| More to come: Under development |
| |
| |
Info Cited from : The World Factbook 2016-17. Washington, DC: Central Intelligence Agency, 2016.
https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html
|








